渔业研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 133-146.DOI: 10.14012/i.cnki.fjsc.2023.02.005
周家丽1,2( ), 傅建融1, 曾嘉维1,2, 陈志劼1,2, 王学锋1,2,*(
), 傅建融1, 曾嘉维1,2, 陈志劼1,2, 王学锋1,2,*( ), 刘丽1,2
), 刘丽1,2
收稿日期:2022-09-13
出版日期:2023-04-25
发布日期:2023-04-19
通讯作者:
王学锋
作者简介:周家丽(1997―),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为海洋污损生物。E-mail: 15218398740@163.com
基金资助:
ZHOU Jiali1,2( ), FU Jianrong1, ZENG Jiawei1,2, CHEN Zhijie1,2, WANG Xuefeng1,2,*(
), FU Jianrong1, ZENG Jiawei1,2, CHEN Zhijie1,2, WANG Xuefeng1,2,*( ), LIU Li1,2
), LIU Li1,2
Received:2022-09-13
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-04-19
Contact:
WANG Xuefeng
摘要:
了解雷州湾海域网衣污损生物群落变化规律,为网箱防污和绿色养殖提供科学依据。2020年6月至2021年6月于雷州湾东南码头养殖网箱中开展上、下水层的周年挂网实验。结果表明,共检出污损生物35种,分属11门28科35属,主要类群包括节肢动物门、软体动物门及绿藻门,冬季污损生物种类最少(7种);全年优势种共有15种,其中上水层12种、下水层15种,上水层的丰度和生物量分别较下水层高8.50 ind·cm-2、0.01 g·cm-2,且上水层污损生物附着量和体型较大;上、下水层总种类数(29~32)、多样性指数(H',0.985~2.010)、均匀度指数(J,0.539~0.852)、丰富度指数(d,0.539~2.856)数值相近;利用Excel和SPSS对56个网衣样本分别进行多样性和单因素方差分析,冬季多样性指数、丰富度指数低于其他季节,但均匀度指数在季节间无明显变化。冗余分析显示,温度(平均贡献率为44.95%)和盐度(平均贡献率为31.90%)是影响污损生物群落结构的主要环境因素。
中图分类号:
周家丽, 傅建融, 曾嘉维, 陈志劼, 王学锋, 刘丽. 雷州湾海域网衣污损生物群落的周年变化特征[J]. 渔业研究, 2023, 45(2): 133-146.
ZHOU Jiali, FU Jianrong, ZENG Jiawei, CHEN Zhijie, WANG Xuefeng, LIU Li. Species composition and seasonal characteristics of the fouling organisms in the cage culturing waters of Leizhou Bay, Guangdong Province[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2023, 45(2): 133-146.
| 门 Phylum | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种类名称 Species | 上水层 Upper water layer | 下水层 Down water layer | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 上半年 First half of the year | 下半年 Second half of the year | 全年 Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节肢 动物门 Arthropoda | 地钩虾科 Podoceridae | 地钩虾属 Podocerus | 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 板钩虾科 Stenothoidae | 板钩虾属 Stenothoe | 加尔板钩虾 Stenothoe gallensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 蜾蠃蜚科 Corophiidae | 蜾蠃蜚属 Corophium | 莫顿蜾蠃蜚 Corophium mortonii | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | |
| 拟钩虾属 Gammaropsis | 指拟钩虾 Gammaropsis digitata | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 藤壶科 Balanidae | 纹藤壶属 Amphibalanus | 网纹藤壶 Amphibalanus reticulatus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 巨藤壶属 Megabalanus | 红巨藤壶 Megabalanus rosa | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — | — | ||
| 节肢 动物门 Arthropoda | 玻璃钩虾科 Hyalidae Bulycheva | 明钩虾属 Parhyale Stebbing | 夏威夷 明钩虾 Parhyale hawaiensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 白钩虾属 Leucothoe Leach | 翼白钩虾 Leucothoe alata | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — | — | ||
| 梭子蟹科 Portunidae Rafinesque | 梭子蟹属 Portunus | 梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 背尾水虱科 Anthuridae | 杯状水虱属 Cyathura | 黑斑胚筒虱 Cyathura peitrates | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 软体 动物门 Mollusca | 拟壳菜蛤科 Dreissenidae | 壳菜蛤属 Dreissena | 斑马纹贻贝 Dreissena polymorpha | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 贻贝科 Mytilidae | 股贻贝属 Perna | 翡翠贻贝 Perna virids | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | |
| 贻贝属 Mytilus | 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | + | + | — | + | + | — | + | — | + | ||
| 短齿蛤属 Brachidontes | 变化短齿蛤 Brachidontes variabilis | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | + | + | ||
| 肌蛤属 Musculus | 凸壳肌蛤 Musculus senhousei | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | ||
| 蚶科 Arcidae | 须蚶属 Barbatia | 珠肋须蚶 Barbatia yamamotoi | + | + | — | — | + | — | — | — | + | |
| 骨螺科 Muricidae | 荔枝螺属 Thais | 砺敌荔枝螺 Thais gradata | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 牡蛎科 Ostreidae | 巨牡蛎属 Crassostrea | 近江牡蛎 Crassostrea rivularis | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 刺胞 动物门 Coelenterata | 笔螅科 Pennariidae | 笔螅属 Pennaria | 笔螅 Pennaria disticha | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + |
| 纵条矶 海葵科 Haliplanellidae | 纵条矶 海葵属 Haliplanella | 纵条矶 海葵 Haliplanella luciae | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 环节 动物门 Annelida | 多鳞虫科 Polynoidae | 海鳞虫属 Halosydna | 短毛海鳞虫 Halosydna nebulosa | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | + | + |
| 金扇虫科 Chrysopetalidae | 卷虫属 Bhawania | 隐头卷虫 Bhawania goodei | + | + | — | + | + | — | + | — | + | |
| 海稚虫科 Spionidae | 才女虫属 Polydora | 才女虫 Polydora sp. | + | + | — | — | — | — | + | — | + | |
| 缨鳃虫科 Sabellidae | 伪刺缨虫属 Pseudopotamilla | 伪刺缨虫 Pseudopotamilla reniformis | — | + | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 棘皮动物门 Echinodermata | 辐蛇尾科 Ophiactidae | 辐蛇尾属 Ophiactis | 近辐蛇尾 Ophiactis affinis | — | + | — | — | + | — | — | — | — |
| 多孔动物门 Porifera | 皮海绵科 Suberitidae | 荔枝海绵属 Tethya | 荔枝海绵 Tethya sp. | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | — | + |
| 纽形动物门 Nemertinea | 纵沟纽虫科 Gorgonorh ynchidae | 纵沟纽虫属 Gorgonorh ynchus | 纵沟纽虫 Gorgonorh ynchus sp. | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | + | + |
| 扁形动物门 Platyhe- lminthes | 扁虫科 Pseudoce- rotidae | 扁虫属 Pseudoceros | 外角伪涡虫 Pseudoceros exoptatus | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + |
| 脊椎动物门 Verbebrata | 塘鳢科 Eleotridae | 塘鳢属 Eleotris | 塘鳢 Eleotris acanthopoma | + | — | — | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 绿藻门 ChloropHyta | 石莼科 Ulvaceae | 浒苔属 Enteromorpha | 浒苔 Enteromorpha prolifera | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + |
| 石莼属 Ulva | 石莼 Ulva lactuca | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | + | + | ||
| 礁膜科 Monos- tromataceae | 礁膜属 Monostroma | 礁膜 Monostroma | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — | + | |
| 红藻门 RhodopHyta | 江蓠科 Ulvaceae | 江蓠属 Gracilaria | 异枝江蓠 Gracilaria bailinae | + | + | + | + | — | — | + | + | + |
| 石花菜科 Gelidiaceae | 石花菜属 Gelidium | 石花菜 Gelidium amansii | + | — | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 红翎菜科 Solieriaceae | 麒麟菜属 Eucheuma | 麒麟菜 Eucheuma muricatum | + | — | — | — | + | — | — | — | — |
表1 东南码头污损生物种类组成
Tab.1 Composition of fouling organisms in the Southeast Wharf
| 门 Phylum | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 种类名称 Species | 上水层 Upper water layer | 下水层 Down water layer | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | 上半年 First half of the year | 下半年 Second half of the year | 全年 Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节肢 动物门 Arthropoda | 地钩虾科 Podoceridae | 地钩虾属 Podocerus | 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 板钩虾科 Stenothoidae | 板钩虾属 Stenothoe | 加尔板钩虾 Stenothoe gallensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 蜾蠃蜚科 Corophiidae | 蜾蠃蜚属 Corophium | 莫顿蜾蠃蜚 Corophium mortonii | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | |
| 拟钩虾属 Gammaropsis | 指拟钩虾 Gammaropsis digitata | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 藤壶科 Balanidae | 纹藤壶属 Amphibalanus | 网纹藤壶 Amphibalanus reticulatus | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 巨藤壶属 Megabalanus | 红巨藤壶 Megabalanus rosa | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — | — | ||
| 节肢 动物门 Arthropoda | 玻璃钩虾科 Hyalidae Bulycheva | 明钩虾属 Parhyale Stebbing | 夏威夷 明钩虾 Parhyale hawaiensis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 白钩虾属 Leucothoe Leach | 翼白钩虾 Leucothoe alata | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — | — | ||
| 梭子蟹科 Portunidae Rafinesque | 梭子蟹属 Portunus | 梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 背尾水虱科 Anthuridae | 杯状水虱属 Cyathura | 黑斑胚筒虱 Cyathura peitrates | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 软体 动物门 Mollusca | 拟壳菜蛤科 Dreissenidae | 壳菜蛤属 Dreissena | 斑马纹贻贝 Dreissena polymorpha | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 贻贝科 Mytilidae | 股贻贝属 Perna | 翡翠贻贝 Perna virids | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + | |
| 贻贝属 Mytilus | 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | + | + | — | + | + | — | + | — | + | ||
| 短齿蛤属 Brachidontes | 变化短齿蛤 Brachidontes variabilis | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | + | + | ||
| 肌蛤属 Musculus | 凸壳肌蛤 Musculus senhousei | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | ||
| 蚶科 Arcidae | 须蚶属 Barbatia | 珠肋须蚶 Barbatia yamamotoi | + | + | — | — | + | — | — | — | + | |
| 骨螺科 Muricidae | 荔枝螺属 Thais | 砺敌荔枝螺 Thais gradata | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 牡蛎科 Ostreidae | 巨牡蛎属 Crassostrea | 近江牡蛎 Crassostrea rivularis | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 刺胞 动物门 Coelenterata | 笔螅科 Pennariidae | 笔螅属 Pennaria | 笔螅 Pennaria disticha | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + |
| 纵条矶 海葵科 Haliplanellidae | 纵条矶 海葵属 Haliplanella | 纵条矶 海葵 Haliplanella luciae | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | |
| 环节 动物门 Annelida | 多鳞虫科 Polynoidae | 海鳞虫属 Halosydna | 短毛海鳞虫 Halosydna nebulosa | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | + | + |
| 金扇虫科 Chrysopetalidae | 卷虫属 Bhawania | 隐头卷虫 Bhawania goodei | + | + | — | + | + | — | + | — | + | |
| 海稚虫科 Spionidae | 才女虫属 Polydora | 才女虫 Polydora sp. | + | + | — | — | — | — | + | — | + | |
| 缨鳃虫科 Sabellidae | 伪刺缨虫属 Pseudopotamilla | 伪刺缨虫 Pseudopotamilla reniformis | — | + | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 棘皮动物门 Echinodermata | 辐蛇尾科 Ophiactidae | 辐蛇尾属 Ophiactis | 近辐蛇尾 Ophiactis affinis | — | + | — | — | + | — | — | — | — |
| 多孔动物门 Porifera | 皮海绵科 Suberitidae | 荔枝海绵属 Tethya | 荔枝海绵 Tethya sp. | + | + | — | + | — | — | — | — | + |
| 纽形动物门 Nemertinea | 纵沟纽虫科 Gorgonorh ynchidae | 纵沟纽虫属 Gorgonorh ynchus | 纵沟纽虫 Gorgonorh ynchus sp. | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | + | + |
| 扁形动物门 Platyhe- lminthes | 扁虫科 Pseudoce- rotidae | 扁虫属 Pseudoceros | 外角伪涡虫 Pseudoceros exoptatus | — | + | — | — | — | — | — | — | + |
| 脊椎动物门 Verbebrata | 塘鳢科 Eleotridae | 塘鳢属 Eleotris | 塘鳢 Eleotris acanthopoma | + | — | — | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 绿藻门 ChloropHyta | 石莼科 Ulvaceae | 浒苔属 Enteromorpha | 浒苔 Enteromorpha prolifera | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | + |
| 石莼属 Ulva | 石莼 Ulva lactuca | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | + | + | ||
| 礁膜科 Monos- tromataceae | 礁膜属 Monostroma | 礁膜 Monostroma | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — | + | |
| 红藻门 RhodopHyta | 江蓠科 Ulvaceae | 江蓠属 Gracilaria | 异枝江蓠 Gracilaria bailinae | + | + | + | + | — | — | + | + | + |
| 石花菜科 Gelidiaceae | 石花菜属 Gelidium | 石花菜 Gelidium amansii | + | — | + | + | — | — | — | — | — | |
| 红翎菜科 Solieriaceae | 麒麟菜属 Eucheuma | 麒麟菜 Eucheuma muricatum | + | — | — | — | + | — | — | — | — |
| 水层 Water layer | 物种名称 Species | 平均密度 /ind·cm-2 Average density | 平均密度 /g·cm-2 Average density | IRI | 生活方式 Lifestyle | 功能性群体 Functional group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上 Upper | 指拟钩虾 Gammaropsis digitata | 14.370 | 0.036 | 4 648 | M | D |
| 网纹藤壶 Amphibalanus reticulatus | 0.982 | 0.183 | 3 948 | SE | S | |
| 加尔板钩虾 Stenothoe gallensis | 5.470 | 0.022 | 1 961 | M | D | |
| 笔螅 Pennaria disticha | 7.700 | 0.008 | 1 845 | SE | S | |
| 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | 4.404 | 0.018 | 1 576 | M | D | |
| 夏威夷明钩虾 Parhyale hawaiensis | 2.512 | 0.016 | 1 024 | M | D | |
| 斑马纹贻贝 Dreissena polymorpha | 0.346 | 0.040 | 853 | A | S | |
| 翡翠贻贝 Perna virids | 0.144 | 0.043 | 729 | A | S | |
| 莫顿蜾蠃蜚 Corophium mortonii | 1.004 | 0.005 | 323 | M | D | |
| 浒苔 Enteromorpha prolifera | 0.214 | 0.009 | 140 | A | PP | |
| 变化短齿蛤 Brachidontes variabilis | 0.176 | 0.021 | 131 | A | S | |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.017 | 0.017 | 71 | A | S | |
| 下 Down | 指拟钩虾 Gammaropsis digitata | 23.120 | 0.031 6 | 3 645 | M | D |
| 加尔板钩虾 Stenothoe gallensis | 11.800 | 0.022 8 | 2 652 | M | D | |
| 网纹藤壶 Amphibalanus reticulatus | 0.740 | 0.114 0 | 2 425 | SE | S | |
| 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | 4.340 | 0.021 6 | 4 473 | M | D | |
| 翡翠贻贝 Perna virids | 0.780 | 0.105 2 | 1 989 | A | S | |
| 笔螅 Pennaria disticha | 7.000 | 0.009 2 | 1 194 | SE | S | |
| 斑马纹贻贝 Dreissena polymorpha | 0.100 | 0.034 8 | 762 | A | S | |
| 莫顿蜾蠃蜚 CoropHium mortonii | 0.000 | 0.005 6 | 585 | M | D | |
| 夏威夷明钩虾 Parhyale hawaiensis | 0.260 | 0.005 6 | 273 | M | D | |
| 下 Down | 石莼 Ulva lactuca | 0.240 | 0.013 2 | 185 | A | PP |
| 红巨藤壶 Megabalanus rosa | 0.000 | 0.016 8 | 117 | SE | S | |
| 变化短齿蛤 Brachidontes variabilis | 0.740 | 0.016 0 | 103 | A | S | |
| 浒苔 EnteromorpHa prolifera | 0.340 | 0.002 8 | 40 | A | PP | |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.080 | 0.018 4 | 31 | A | S | |
| 异枝江蓠 Gracilaria bailinae | 0.130 | 0.001 1 | 25 | A | PP |
表2 网衣污损生物优势种
Tab.2 Fouling biological dominant species of net
| 水层 Water layer | 物种名称 Species | 平均密度 /ind·cm-2 Average density | 平均密度 /g·cm-2 Average density | IRI | 生活方式 Lifestyle | 功能性群体 Functional group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上 Upper | 指拟钩虾 Gammaropsis digitata | 14.370 | 0.036 | 4 648 | M | D |
| 网纹藤壶 Amphibalanus reticulatus | 0.982 | 0.183 | 3 948 | SE | S | |
| 加尔板钩虾 Stenothoe gallensis | 5.470 | 0.022 | 1 961 | M | D | |
| 笔螅 Pennaria disticha | 7.700 | 0.008 | 1 845 | SE | S | |
| 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | 4.404 | 0.018 | 1 576 | M | D | |
| 夏威夷明钩虾 Parhyale hawaiensis | 2.512 | 0.016 | 1 024 | M | D | |
| 斑马纹贻贝 Dreissena polymorpha | 0.346 | 0.040 | 853 | A | S | |
| 翡翠贻贝 Perna virids | 0.144 | 0.043 | 729 | A | S | |
| 莫顿蜾蠃蜚 Corophium mortonii | 1.004 | 0.005 | 323 | M | D | |
| 浒苔 Enteromorpha prolifera | 0.214 | 0.009 | 140 | A | PP | |
| 变化短齿蛤 Brachidontes variabilis | 0.176 | 0.021 | 131 | A | S | |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.017 | 0.017 | 71 | A | S | |
| 下 Down | 指拟钩虾 Gammaropsis digitata | 23.120 | 0.031 6 | 3 645 | M | D |
| 加尔板钩虾 Stenothoe gallensis | 11.800 | 0.022 8 | 2 652 | M | D | |
| 网纹藤壶 Amphibalanus reticulatus | 0.740 | 0.114 0 | 2 425 | SE | S | |
| 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | 4.340 | 0.021 6 | 4 473 | M | D | |
| 翡翠贻贝 Perna virids | 0.780 | 0.105 2 | 1 989 | A | S | |
| 笔螅 Pennaria disticha | 7.000 | 0.009 2 | 1 194 | SE | S | |
| 斑马纹贻贝 Dreissena polymorpha | 0.100 | 0.034 8 | 762 | A | S | |
| 莫顿蜾蠃蜚 CoropHium mortonii | 0.000 | 0.005 6 | 585 | M | D | |
| 夏威夷明钩虾 Parhyale hawaiensis | 0.260 | 0.005 6 | 273 | M | D | |
| 下 Down | 石莼 Ulva lactuca | 0.240 | 0.013 2 | 185 | A | PP |
| 红巨藤壶 Megabalanus rosa | 0.000 | 0.016 8 | 117 | SE | S | |
| 变化短齿蛤 Brachidontes variabilis | 0.740 | 0.016 0 | 103 | A | S | |
| 浒苔 EnteromorpHa prolifera | 0.340 | 0.002 8 | 40 | A | PP | |
| 厚壳贻贝 Mytilus coruscus | 0.080 | 0.018 4 | 31 | A | S | |
| 异枝江蓠 Gracilaria bailinae | 0.130 | 0.001 1 | 25 | A | PP |
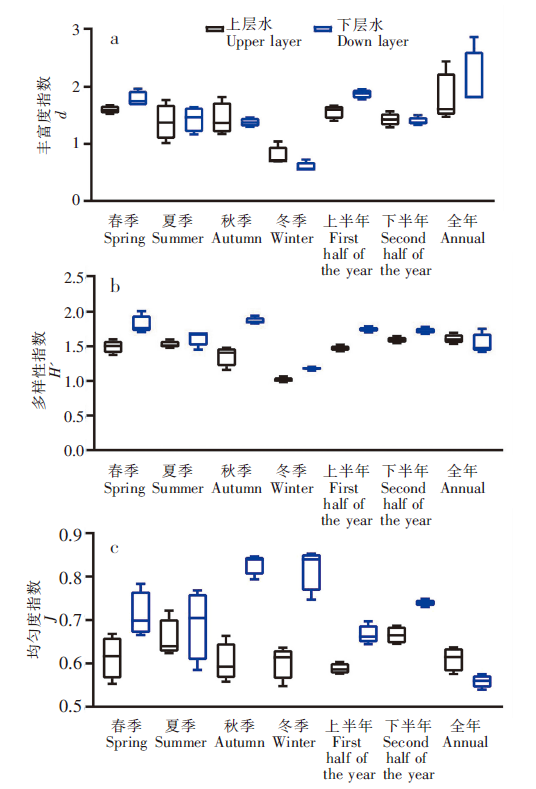
图5 不同观测周期网衣污损生物多样性变化[丰富度指数(a)、多样性指数(b)、均匀度指数(c)]
Fig.5 Variation of species diversity of net fouling organisms in different observing periods[Margalef index (a),Shannon-Wiener index(b),Pielou index(c)]
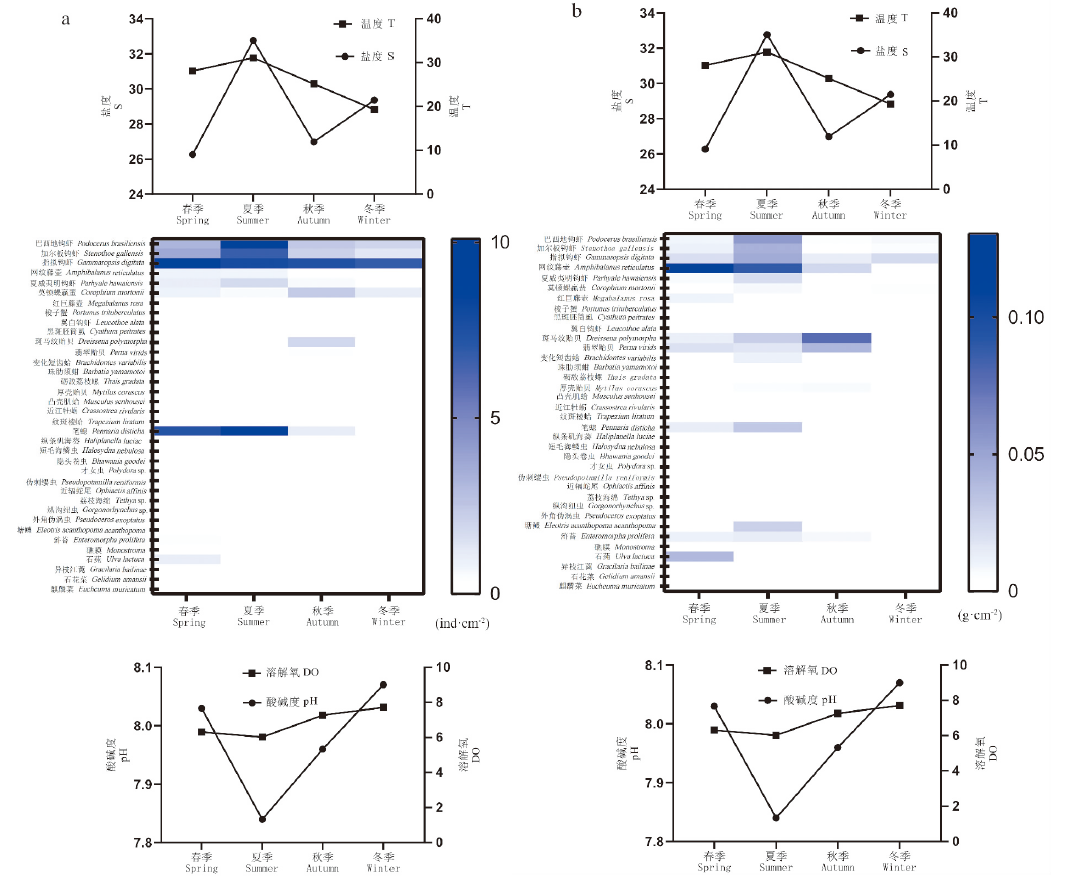
图6 不同观测季节网衣污损生物的丰度(a)和生物量(b)与环境因子的变化情况
Fig.6 Changes of the abundance (a) and biomass (b) of fouling organisms and environmental factors in different observing seasons
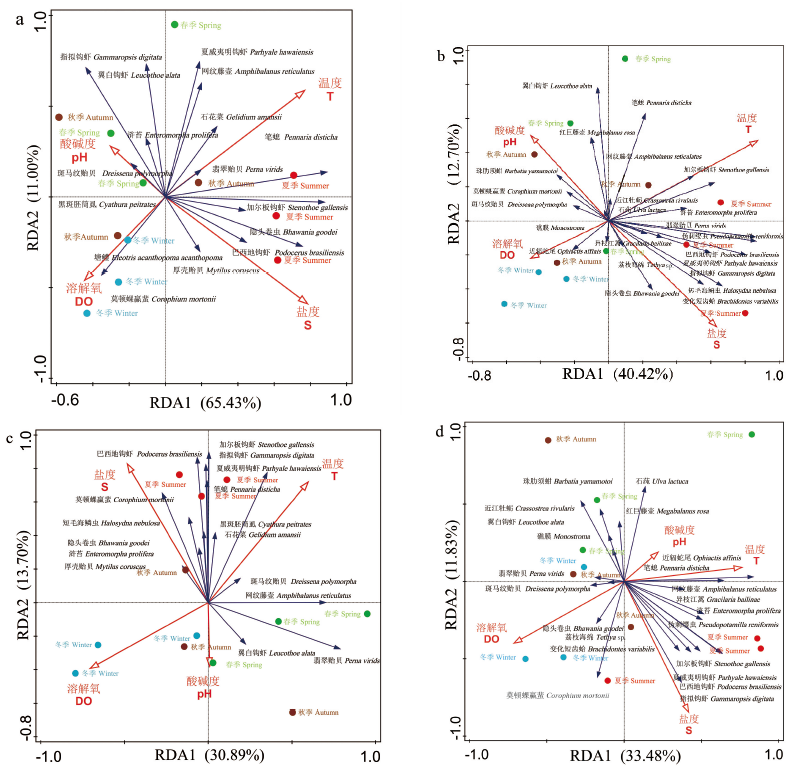
图7 不同观测时期网衣污损生物群落与环境因子RDA 分析,丰度上水层(a)、下水层(b),生物量上水层(c)、下水层(d)
Fig.7 RDA analysis of cage fouling biological community and environmental factors in different observing periods, the abundance upper water layer(a) and down water layer(b), the biomass upper water layer(c) and down water layer(d)
| [1] | 张凯, 丛巍巍, 桂泰江, 等. 海洋水产养殖业中的生物污损与控制[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(S1):78-81. |
| [2] | 小远. 2018世界渔业和水产养殖状况报告[J]. 渔业致富指南, 2018(21):6-7. |
| [3] | 宋协法, 孙跃, 何佳, 等. 深水网箱清洗技术及装备研究进展[J]. 渔业现代化, 2021, 48(5):1-9. |
| [4] | 石建高, 余雯雯, 赵奎, 等. 海水网箱网衣防污技术的研究进展[J]. 水产学报, 2021, 45(3):472-485. |
| [5] | 郑东强, 黄宗国. 大亚湾海水养殖箱、笼上附着的污损生物[J]. 水产学报, 1990(1):15-24. |
| [6] |
Sen K, Erdogan U H, Cavas L. Prevention of biofouling on aquaculture nets with ecofriendly antifouling paint formulation[J]. Coloration Technology, 2020, 136(2):120-129.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 陈志劼, 吕少梁, 陆丽仪, 等. 雷州半岛东部近岸海域大型底栖甲壳动物群落结构及其影响因子[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2021, 41(1):17-25. |
| [8] | 刘苏静. 烟台近海海域典型污损生物调查及其防除研究[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所, 2016. |
| [9] | 刘勐伶, 严涛. 南海污损生物生态研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 2006, 25(1):84-91. |
| [10] | 方芳, 严涛. 南海污损生物研究的现状及展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2004, 23(1):76-85. |
| [11] | 胡煜峰, 曹文浩, 张慧, 等. 近海污损生物生态研究及建议[J]. 广州化工, 2012, 40(21):6-7. |
| [12] | 陈新, 曹阳, 商群, 等. 南海近岸污损生物群落时空差异初步研究[C]// 中国海洋湖沼学会.中国海洋湖沼学会第十次会员代表大会暨2012海洋腐蚀与生物污损学术研讨会论文集. 青岛: 中国海洋湖沼学会, 2012:12. |
| [13] | 曾嘉维, 林坤, 王学锋, 等. 雷州湾附近海域鱼类群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(1):108-117. |
| [14] | 陈春亮, 张才学. 雷州湾浮游植物群落结构特征及其环境影响分析[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2016, 35(2):174-182. |
| [15] | 任先秋. 中国动物志:无脊椎动物第41卷甲壳动物亚门端足目钩虾亚目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. |
| [16] | 任先秋. 中国动物志:无脊椎动物第43卷甲壳动物亚门端足目钩虾亚目 2[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. |
| [17] | 刘瑞玉, 任先秋. 中国动物志:无脊椎动物第42卷甲壳动物亚门蔓足下纲围胸总目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. |
| [18] | 王祯瑞. 中国动物志:软体动物门双壳纲贻贝目[J]. 科学出版社, 1997. |
| [19] | Flanders Marine Institute. 世界海洋物种登记网址[DB/OL].(2022-11-05)[2022-10-01]. https://www.marinespecies.org/. |
| [20] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋调查规范第6部分:海洋调查资料交换:GB/T 1276.6—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. |
| [21] | Pinkas L, Oliphant M S, Iverson I L K. 1971.Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters[J]. Fish Bulletin, 152:1-105. |
| [22] |
Greene J K, Grizzle R E. Successional development of fouling communities on open ocean aquaculture fish cages in the western Gulf of Maine, USA[J]. Aquaculture, 2007, 262(2-4):289-301.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 水柏年, 郭迪飞. 舟山深水网箱污损生物季节性变化分析[J]. 南方水产科学, 2008, 4(4):36-41. |
| [24] |
Bosch-Belmar M, Escurriola A, Milisenda G, et al. Harmful fouling communities on fish farms in the SW Mediterranean Sea: composition, growth and reproductive periods[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2019, 7(9):288.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Sliskovic M, Jelic-Mrcelic G, Antolic B, et al. The fouling of fish farm cage nets as bioindicator of aquaculture pollution in the Adriatic Sea (Croatia)[J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2011, 173(1-4):519-532. |
| [26] |
Lin H S, Wang J J, Liu W, et al. Fouling community characteristics in subtropical coastal waters of the southwestern East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(10):70-78.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Yan T, Yan W, Dong Y, et al. Marine fouling of offshore installations in the northern Beibu Gulf of China[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2006, 58(2):99-105. |
| [28] | Amini N, Rezai H, Pourjomeh F, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of biofouling on the oil platforms around Khark Island, Persian Gulf[J]. Indian journal of marine sciences, 2016, 45(12):1714-1718. |
| [29] | Ramadan S E, Kheirallah A M, Abdel-Salam K M. Marine fouling community in the Eastern harbour of Alexandria, Egypt compared with four decades of previous studies[J]. Mediterranean Marineence, 2006, 7(2):19-29. |
| [30] |
Ramadan S E, Kheirallah A M, Abdelsalam K M. Factors controlling marine fouling in some Alexandria Harbours, Egypt[J]. Mediterranean Marine Science, 2012, 7(2):31-54.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 黄桂芳, 郑国富, 魏观渊, 等. 福建围头海域深水网箱养殖区污损生物[J]. 海洋学报, 2007, 29(1):98-104. |
| [32] | 君珊, 王东波, 周健华, 等. 拉萨河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(3):787-798. |
| [33] | 严涛, 曹文浩. 黄、渤海污损生物生态特点及研究展望[J]. 海洋学研究, 2008, 26(3):107-118. |
| [34] | Dziubińska A, Janas U. Submerged objects - a nice place to live and develop.Succession of fouling communities in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic[J]. Oceanological & Hydrobiological Studies, 2007, 36(4):65-78. |
| [35] |
Nogata Y, Tokikuni N, Yoshimura E, et al. Salinity limitations on larval settlement of four barnacle species[J]. Sessile Organisms, 2011, 28(2):47-54.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
曹文浩, 严瑾, 丰美萍, 等. 盐度对中国东南沿海两种常见藤壶幼虫发育的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(6):85-91.
DOI |
| [1] | 何美峰 肖九兰 梁忠连 崔利峰 陈梦云. 泰宁金湖鱼类群落结构及鲢、鳙生长特征[J]. 渔业研究, 2023, 45(5): 462-472. |
| [2] | 游剑涛. 三沙湾及邻近开放海域夏季浮游植物群落结构比较[J]. 渔业研究, 2022, 44(6): 581-587. |
| [3] | 刘勇 马超 赵文武 翁祖桐 徐春燕 庄之栋 蔡建堤 谢少卿 沈长春. 闽江口及附近海域春夏季鱼类群落结构特征[J]. 渔业研究, 2022, 44(5): 467-476. |
| [4] | 邹双燕. 平潭近岸海域春、夏季浮游植物特征及其与环境因子相关性分析[J]. 渔业研究, 2022, 44(3): 266-274. |
| [5] | 向佳丽 李渊 宋普庆 刘世刚 王芮 李海 妙星 张然 林龙山. 鱼类肠道微生物多样性及其与环境因子关系的研究进展[J]. 渔业研究, 2022, 44(2): 187-195. |
| [6] | 林建杰. 闽江口潮间带大型底栖动物群落基本特征分析[J]. 渔业研究, 2022, 44(1): 33-43. |
| [7] | 戴红 邱茂福 杨毕铖 戴桂香. 闽江口以南海域夏季浮游植物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. , 2016, 38(1): 56-66. |
| [8] | 张光星 吴钟解 陈石泉 蔡泽富 王道儒. 春季三亚湾浮游动物生态特征与环境因子的关系[J]. 福建水产, 2014, 36(3): 176-184. |
| [9] | 陈宇锋 陈小红 陈月忠 钟硕良. 春、夏两季东山湾不同区域异养细菌的分布及其影响因子[J]. , 2014, 36(2): 110-118. |
| [10] | 张玉荣 丁跃平 郭远明 李铁军 薛彬 鲍静娇 朱剑. 乐清湾浮游植物群落结构调查研究[J]. 福建水产, 2013, 35(4): 249-257. |
| [11] | 肖莹. 闽江口海域浮游植物群落结构特征[J]. 福建水产, 2013, 35(4): 258-263. |
| [12] | 马超 沈长春 刘勇. 罗源湾夏季游泳动物种类组成及其多样性[J]. 福建水产, 2012, 34(6): 449-454. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||