Polymorphisms of MC4R gene and its association with growth traits in Neolissochilus benasi
-
摘要:背景
软鳍新光唇鱼(Neolissochilus benasi)是重要的水产种质资源,但在培育过程中存在个体间生长速度差异较大的问题。
目的筛选与软鳍新光唇鱼生长性状显著相关的分子标记,推动其生长性状的改良。
方法本研究对与摄食、能量代谢、生长发育密切相关的黑素皮质素受体-4(MC4R)基因开展研究,通过PCR-Sanger测序技术进行单核苷酸多态性(SNP)检测和分型,并将SNP位点与其生长性状进行关联性分析,挖掘软鳍新光唇鱼生长性状关联的SNP标记。
结果MC4R基因2个拷贝共存在15个SNP位点,其中第1个拷贝有1个SNP位点,第2个拷贝有14个SNP位点。15个SNP位点中仅G227A为错义突变,氨基酸类型由缬氨酸(V)变为异亮氨酸(I),其余位点均为同义突变;群体遗传分析结果显示,除第1个拷贝SNP位点G669C 遗传参数值较低外,MC4R基因第2个拷贝的SNP位点期望杂合度 (He)和观测杂合度(Ho)分别为0.860±0.027和0.503±0.001,多态信息含量(PIC)为0.373~0.375,属于中度多态性,表明该群体的遗传多样性处于中上水平;关联性分析显示,MC4R基因2个拷贝15个SNP位点中,13个位点对软鳍新光唇鱼的生长性状具有不同程度的影响:位点G227A、A322G、C364T、G403A、T451C、G457A、G472A、T484C、G520A、T583C、G736A、C775G与体长、体质量显著相关(P<0.05),且均以纯合子为优势基因型,分别为AA、GG、TT、AA、CC、AA、AA、CC、AA、CC、AA、GG型;位点C664T仅检测到CC和CT两种基因型,并以杂合子CT型为优势基因型,与体质量显著相关(P<0.05)。
结论本研究初步筛选了15个与软鳍新光唇鱼生长性状相关联的候选SNP位点,为今后其生长相关机制和分子标记的进一步解析,以及生长性状的改良提供了科学依据。
Abstract:BackgroundNeolissochilus benasi is an important aquatic germplasm resource, but there is a problem of large differences in growth rate among individuals during the breeding process.
ObjectiveThe study aims to identify molecular markers significantly associated with the growth traits in N. benasi and promote the improvement of its growth characteristics.
MethodsThe study focused on melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) gene, which are deeply related to ingestion, energy metabolism and growth development. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection and genotyping were performed using PCR-Sanger sequencing technology, and association analysis was conducted between the SNP loci and growth traits to identify SNP markers related to the growth traits of N. benasi.
ResultsThe results showed that there were 15 SNP loci in the two copies of MC4R gene, with one SNP locus in the first copy and 14 SNP loci in the second copy. Among the 15 SNP loci, only G227A was a missense mutation, with the amino acid type changed from valine (V) to isoleucine (I). The remaining loci were synonymous mutations. Population genetic analysis showed that, except for SNP locus G669C in the first copy with low genetic parameter values, the SNP loci in the second copy of MC4R gene had an expected heterozygosity (He) and observed heterozygosity (Ho) of 0.860 4±0.027 2 and 0.503 2±0.001 4, respectively, and their polymorphic information content (PIC) ranged from
0.3731 to0.3749 , indicating a middle-upper level of genetic diversity in this population. Association analysis revealed that 13 SNP loci in the two copies of MC4R gene had varying degrees of influence on the growth traits of N. benasi: G227A, A322G, C364T, G403A, T451C, G457A, G472A, T484C, G520A, T583C, G736A, and C775G were significantly associated with body length and body mass (P<0.05), with homozygous genotypes AA, GG, TT, AA, CC, AA, AA, CC, AA, CC, AA, and GG being the dominant genotypes, respectively. Meanwhile, C664T was only detected two genotypes (CC and CT), with the heterozygous CT genotype being dominant and strongly associated with body mass (P<0.05).ConclusionThis study preliminarily screens 15 candidate SNP loci associated with growth traits in N. benasi, providing a scientific basis for further analysis of growth-related mechanisms and molecular markers, as well as for the improvement of growth traits in this species.
-
软鳍新光唇鱼(Neolissochilus benasi)隶属于鲤形目(Cypriniformes)、鲤科(Cyprinidae)、新光唇鱼属(Neolissochilus),是红河水系特有珍稀鱼类,在中国主要分布于元江、李仙江流域[1]。由于大规模水利建设、鱼类资源利用强度增加、保护意识薄弱等原因,软鳍新光唇鱼野外种群数量急剧下降[2],目前仅在云南江城县和西畴县保留有较大种群[3]。中国科学院昆明动物研究所经过长期努力,突破了软鳍新光唇鱼的精子超低温冷冻保存[4]和人工繁殖技术[5],有效避免了该物种的灭绝,且人工繁殖的成功,为其可持续利用奠定了坚实的基础。在人工繁育的基础上,经过4代群体选育,复杂肌间刺弱化的软鳍新光唇鱼“墨龙1号”于2022年获得农业农村部的新品种认证,为云南乃至中国水产养殖业的发展提供了良好的种质资源。
然而,养殖过程中个体间生长速度差异大等问题仍然对产业化发展具有较大制约作用[6]。因此,选育生长速度快的稳定品系是推动其产业化发展的重要环节。近年来,分子生物学技术的飞速发展,促使分子辅助育种成为当前选择育种的热门方法[7],而获取高效、可识别性强的分子标记是分子辅助育种的前提。已有研究表明,生长是典型的数量性状,受多种基因的共同调控,并且不同物种生长相关调控机制、主效调控基因和关键调控元件不尽相同[8]。因此,对特定物种开展生长相关分子标记的筛选是推动优良品种选育的前提。
黑素皮质素受体-4(Melanocortin-4 receptor,MC4R)是下丘脑腹内侧核分泌的一种肽类物质[9],可与垂体分泌的内源性激动剂α-促黑素细胞激素(Alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone,α-MSH)及其拮抗剂agouti相关蛋白(Agouti related protein,AGRP)结合,以调节食欲和摄食行为、控制能量稳态[10-11]。作为重要的食欲调节基因,MC4R在中枢神经系统高度表达,对动物生长发育具有重要调控作用[12-14]。动物MC4R基因多态性研究已发现多个单核苷酸多态性(Single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)位点,与动物体长、体质量等生长表型显著相关[15-16],但其在软鳍新光唇鱼生长发育中的调控作用研究尚未报道,与其相关的显著分子标记仍有待挖掘。因此,本研究通过PCR-Sanger测序技术对软鳍新光唇鱼MC4R基因进行SNP位点检测,并进行关联性分析,筛选出与软鳍新光唇鱼生长性状显著相关的SNP位点及其优势基因型,旨在为软鳍新光唇鱼的良种培育发掘具有较高应用潜力的SNP位点,同时为鱼类MC4R基因的进一步研究提供基础数据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 样品采集与数据测量
实验所用样本为养殖于中国科学院昆明动物研究所珍稀鱼类繁殖基地,于相同饲养环境和管理方法下长成的同一家系的6月龄软鳍新光唇鱼。通过对该家系所有样本进行体长、全长、体质量的测量,表型数据呈正态分布。选择分布于两端的50尾极端大个体[平均体长为(107.80±4.72)mm,体质量为(25.48±3.37)g],50尾极端小个体[平均体长为(56.84±3.16)mm、体质量为(3.45±0.55)g],剪取鳍条组织浸泡于无水乙醇中,放置在−20 ℃冰箱中保存,用于后续实验。体长、全长采用游标卡尺(精度0.01 mm)测量,体质量采用电子天平(精度0.01 g)测量。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 组织DNA提取
取出鱼鳍组织样品,使用异丙醇DNA提取法[17-18]提取100个鱼鳍样品的DNA,并于4 ℃溶解过夜后,放置在−20 ℃冰箱中保存。中国科学院昆明动物研究所生命科学伦理委员会批准动物实验,批准编号为SMKX-SQ-2021-111。
1.2.2 引物设计与PCR扩增
根据软鳍新光唇鱼基因组中MC4R基因编码区序列(Coding sequence,CDS)(NCBI序列号:PQ682452,PQ682453),采用Primer Premier 5.0 (Premier Biosoft International)软件设计引物,引物送至昆明擎科生物有限公司合成。通过筛选并选取5个样本进行预实验,以验证引物的特异性,最终确定M1、M2两对引物用于MC4R基因2个拷贝的扩增,扩增目的片段度分别为1 027、1 050 bp。引物序列详情见表1。扩增反应总体系为25 μL,包括基因组DNA模板1 μL,上下游引物各1 μL,power POL 2 PCR mix (爱博泰克生物科技有限公司,武汉)12.5 μL,dH2O(无菌去离子水) 9.5 μL;PCR反应程序:94 ℃预变性3 min,30个扩增循环(94 ℃变性30 s;55 ℃退火30 s;72 ℃延伸1 min),最后72 ℃延伸5 min。
表 1 软鳍新光唇鱼PCR引物信息Table 1. Primers used in the amplification of N. benasi目标基因
Gene of interest引物
Primers序列(5’-3’ )
Sequence (5’-3’)退火温度/℃
Annealing temperature产物长度/bp
Product lengthMC4R M1 F:AAACCACTGACTACGGATAT
R:CGTCAAACAGAAACAAGC55 1 027 M2 F:AAACCACTGACTACGGATAT
R:TTGCTTAGTGTTGTCTTGC55 1 050 1.3 统计分析
1.3.1 SNP位点筛选及分型
扩增产物送至昆明擎科生物有限公司进行测序,本研究采用直接测序法。将返回产物序列用DNAStar 7.1软件包中的SeqMan 7.1.0[19]软件进行剪切、拼接,根据测序峰图确定SNP位点并按照单双峰型划分各位点的基因型,并通过Emboss transeq在线工具(https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/st/emboss_transeq/)对MC4R基因2个拷贝的SNP位点进行氨基酸突变分析。
1.3.2 群体遗传学分析
统计不同基因型的样本数量,并利用Popgene 1.32[20]、Power Marker[21]软件进行群体遗传学分析,包括计算各基因位点的基因型频率、等位基因频率、有效等位基因数(Effective number of alleles,Ne)、期望杂合度(Expected heterozygosity,He)、观测杂合度(Observed heterozygosity,Ho)、多态信息含量(Polymorphism information content,PIC)、固定指数(Fixation index,Fis),以及通过X2分析进行哈代温伯格(Hardy-Weinberg,HWE)平衡检验,X2<5.991为HWE平衡,X2>5.991为偏离HWE平衡。
1.3.3 生长性状关联性分析
运用SPSS 26.0[22]统计软件将各样本基因型与生长性状进行关联分析,对符合Levene’s test和正态分布的位点进行单因素方差分析,事后检验通过Duncan’s test进行;反之,则采取非参数检验,事后多重比较通过Kruskal-Wallis test进行,以分析各基因型相关的表型间的差异显著性。结果均采用平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 SNP位点检测
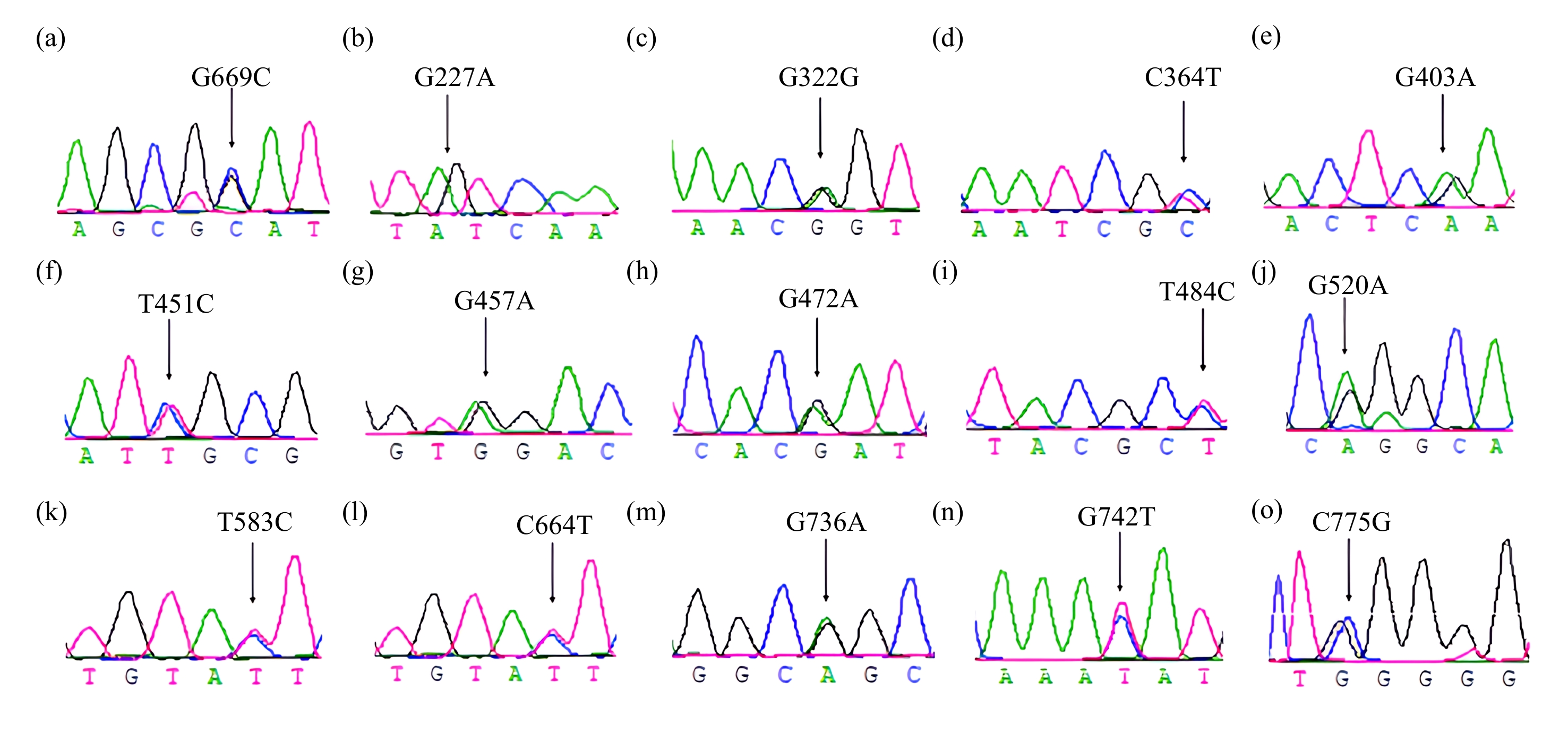
对PCR扩增产物测序后,MC4R基因2个拷贝各有82条和69条序列用于多态性检测。结果显示:MC4R第1个拷贝有1个SNP位点,为位于669 bp处的G669C;第2个拷贝有14个SNP位点,分别是位于227、322、403、457、472、520、736 bp处的G/A突变,位于364、451、484、583、664、742 bp处的C/T突变,以及位于775 bp处的C/G突变;各位点测序峰图结果见图1。
氨基酸突变分析结果显示:第1个拷贝序列中G669C突变点为同义突变,编码氨基酸为精氨酸(R);第2个拷贝发现的14个SNP位点中,仅位点G227A为错义突变,氨基酸类型由缬氨酸 (V)变为异亮氨酸(I),其余位点均为同义突变,未发生氨基酸改变,具体信息见表2。
表 2 MC4R基因两个拷贝SNP位点的氨基酸突变Table 2. Amino acid mutations at various SNP loci in two copies of the MC4R gene位点
Loci突变序列
Mutant sequences突变氨基酸类型
Types of mutant amino acid突变区
RegionG669C CGG→CGC R-R 精氨酸 exon G227A GTC→ATC V-I 缬氨酸−异亮氨酸 exon A322G ACA→ACG T-T 苏氨酸 exon C364T CGC→CGT R-R 精氨酸 exon G403A TCG→TCA S-S 丝氨酸 exon T451C ATT→ATC I-I 异亮氨酸 exon G457A GTG→GTA V-V 缬氨酸 exon G472A ACG→ACA T-T 苏氨酸 exon T484C GCT→GCC A-A 丙氨酸 exon G520A GCG→GCA A-A 丙氨酸 exon T583C TAT→TAC Y-Y 酪氨酸 exon C664T CAC→CAT H-H 组氨酸 exon G736A GCG→GCA A-A 丙氨酸 exon C742T AAC→AAT N-N 天冬酰胺 exon C775G CTC→CTG L-L 亮氨酸 exon 2.2 SNP位点的遗传多样性分析
MC4R基因筛选出15个SNP位点在软鳍新光唇鱼群体中的遗传参数结果见表3。第1个拷贝SNP位点G669C总体遗传参数值在15个SNP位点中较低,其Ne为1.443,He和Ho分别为0.309和0.351,PIC为0.260;第2个拷贝14个SNP位点有效等位基因数为1.981~2.000,各位点有效等位基因数与观测值接近,表明软鳍新光唇鱼种群各等位基因分布均匀[23],Ho和He分别为0.860±0.027、0.503±0.001,PIC为0.373~0.375,根据Botstein等[24]的标准,当0.25<PIC<0.50,为中度多态性,因此15个SNP位点均处于中度多态。X2检测结果显示,除第1个拷贝G669C位点外,第2个拷贝所有位点均显著偏离Hardy-Weinberg平衡(P<0.05)。各位点基因型频率结果显示,突变点G669C以纯合子GG占比更高,Fis值为−0.145,剩余位点均以杂合型个体占比更高,Fis值范围为−0.841~−0.625。
表 3 MC4R基因两个拷贝各SNP位点群体遗传信息Table 3. Population genetic information of each SNP locus of two copies of MC4R gene位点
Loci样本数
Number基因型(频率)
Genotypes (frequency)等位基因(频率)
Aelles (frequency)HWE Ne Ho He Fis PIC G669C 74 GG(0.635)
GC(0.351)
CC(0.014)C(0.189)
G(0.811)X2=1.443
(P=0.230)1.443 0.351 0.309 −0.145 0.260 G227A 65 AA(0.064)
GG(0.095)
GA(0.841)G(0.516)
A(0.484)X2=28.813
(P=0.000)1.998 0.841 0.504 −0.684 0.375 A322G 65 AA(0.077)
GG(0.062)
GA(0.861)G(0.492)
A(0.507)X2=33.300
(P=0.000)2.000 0.862 0.504 −0.724 0.375 C364T 53 CC(0.113)
TT(0.076)
CT(0.811)C(0.519)
T(0.481)X2=20.077
(P=0.000)1.997 0.811 0.504 −0.625 0.375 G403A 66 GG(0.106)
AA(0.061)
GA(0.833)C(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=28.970
(P=0.000)1.996 0.833 0.503 −0.670 0.375 T451C 65 CC(0.062)
TT(0.077)
CT(0.861)C(0.476)
A(0.524)X2=33.300
(P=0.000)2.000 0.862 0.504 −0.724 0.375 G457A 66 GG(0.076)
GA(0.864)
AA(0.060)G(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=34.220
(P=0.000)2.000 0.864 0.504 −0.728 0.375 G472A 62 GG(0.081)
GA(0.855)
AA(0.064)G(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=30.555
(P=0.000)2.000 0.855 0.504 −0.841 0.373 T484C 64 CC(0.062)
TT(0.078)
CT(0.860)C(0.492)
T(0.508)X2=32.383
(P=0.000)2.000 0.859 0.504 −0.719 0.375 G520A 63 GG(0.063)
AA(0.080)
GA(0.857)G(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=31.468
(P=0.000)2.000 0.857 0.504 −0.715 0.375 T583C 59 CC(0.068)
TT(0.085)
CT(0.847)C(0.492)
T(0.508)X2=27.837
(P=0.000)1.999 0.848 0.504 −0.695 0.375 C664T 62 CC(0.097)
CT(0.903)C(0.548)
T(0.452)X2=41.238
(P=0.000)1.981 0.903 0.499 −0.824 0.373 G736A 66 GG(0.076)
AA(0.061)
GA(0.863)G(0.492)
A(0.508)X2=34.220
(P=0.000)2.000 0.864 0.504 −0.728 0.375 C742T 66 CC(0.076)
CT(0.924)C(0.540)
T(0.460)X2=47.867
(P=0.000)1.989 0.924 0.501 −0.826 0.374 C775G 66 CC(0.076)
GG(0.061)
GC(0.863)C(0.508)
G(0.492)X2=34.220
(P=0.000)2.000 0.864 0.504 −0.728 0.375 注:HWE为哈代温伯格平衡;He为期望杂合度;Ho为观测杂合度;Ne为有效等位基因数;PIC为多态信息含量;Fis为固定指数。 Notes: HWE indicates Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium; He indicates expected heterozygosity; Ho indicates observed heterozygosity; Ne indicates eff-ective number of alleles; PIC indicates polymorphism information content; Fis indicates fixation index. 2.3 SNP位点与生长性状关联性分析
MC4R基因2个拷贝检测出的15个SNP位点与软鳍新光唇鱼生长性状的关联性分析结果见表4。第1个拷贝G669C位点有3种基因型,CC型个体的质量、体长和全长均高于GC型与GG型个体,但未达到显著性水平(P>0.05)。第2个拷贝C664T、C742T位点仅具有CC、CT两种基因型,关联性分析结果显示,CT杂合型的体长、体质量、全长均优于CC纯合型,C664T处不同基因型个体的体质量呈显著差异(P<0.05),而体长与全长差异不显著;位点C742T不同基因型个体之间性状差异均不显著。第2个拷贝中G227A、C364T、G403A、G472A、T484C、T583C位点均有3种基因型,不同基因型个体体长、全长、体质量间存在显著差异(P<0.05),分别以纯合子AA、TT、AA、AA、CC、CC为优势基因型;位点A322G、T451C、G457A、G520A、G736A、C775G也存在三种基因型,并以纯合型的性状指标高于杂合型,但未在全长上表现出显著差异(P>0.05)。
表 4 MC4R基因两个拷贝SNP位点各基因型与生长性状关联性分析Table 4. Association analysis between different genotypes of loci of two copies of SNP MC4R gene and growth traits位点
Loci基因型(样本量)
Genotype(n)体质量/g
Body mass体长/mm
Body length全长/mm
Total lengthG669C GC(26)
GG(47)
CC(1)8.55±9.55a
14.25±10.97a
27.84±0.00a68.78±22.35a
82.89±26.30a
106.90±0.00a85.66±26.87a
101.69±30.29a
132.73±0.00aG227A GG(6)
AA(4)
GA(53)3.59±0.46b
26.13±2.13a
13.77±10.93b58.73±2.02b
109.92±5.41a
81.06±25.56b74.12±2.89b
134.23±5.46a
100.71±30.81bA322G AA(5)
GG(4)
GA(56)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
13.67±10.96b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
80.81±25.52b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
100.44±30.72aC364T CC(6)
CT(43)
TT(4)3.58±0.46b
14.82±10.96b
26.13±2.13a59.00±1.90b
83.70±25.32b
109.92±5.41a74.42±2.82b
103.80±30.42b
134.23±5.46aG403A GG(7)
GA(55)
AA(4)3.66±0.45b
13.85±10.98b
26.13±2.13a59.29±1.81b
81.19±25.60b
109.92±5.41a74.60±2.64b
100.88±30.82b
134.23±5.46aT451C TT(5)
CT(56)
CC(4)3.57±0.51b
13.31±10.94b
26.13±2.13a59.02±2.12b
79.98±25.44b
109.92±5.41a74.38±3.15a
99.43±30.63a
134.23±5.46aG457A GG(5)
GA(57)
AA(4)3.57±0.51b
13.50±10.94b
26.13±2.13a59.02±2.12b
80.44±25.45b
109.92±5.41a74.38±3.15a
99.98±30.64a
134.23±5.46aG472A GG(5)
GA(53)
AA(4)3.57±0.51b
13.73±10.88b
26.13±2.13a59.02±2.12b
80.89±25.49b
109.92±5.41a74.38±3.15b
100.49±30.67b
134.23±5.46aT484C CC(4)
TT(5)
CT(55)26.13±2.13a
3.57±0.51b
12.86±10.59b109.92±5.41a
59.02±2.12b
79.19±25.01b134.23±5.46a
74.38±3.15b
98.44±30.07bG520A GG(5)
AA(4)
GA(54)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
12.86±10.81b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
79.06±25.40b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
98.27±30.54aT583C CC(4)
TT(5)
CT(50)26.13±2.13a
3.57±0.51b
12.70±10.83b109.92±5.41a
59.02±2.12b
78.51±25.34b134.23±5.46a
74.38±3.15b
97.60±30.47bC664T CC(6)
CT(56)3.41±0.60b
14.64±11.14a58.21±2.75a
83.01±25.96a73.50±3.55a
102.90±31.09aG736A GG(5)
AA(4)
GA(57)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
13.50±10.94b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
80.44±25.45b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
99.98±30.64aC742T CC(5)
CT(61)3.57±0.51a
14.33±11.04a59.02±2.12a
82.37±25.69a74.38±3.15a
102.22±30.83aC775G CC(5)
GG(4)
GC(57)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
13.50±10.94b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
80.44±25.45b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
99.98±30.64a注:同一位点同一指标不同上标小写字母表示组内差异显著(P<0.05),相同上标字母表示组内差异不显著(P>0.05)。 Note: Different superscript lowercase letters in the same column of locus indicate significant difference within the group (P<0.05), and the same superscript lowercase letters indicate no significant differences within the group (P>0.05). 3. 讨论
3.1 软鳍新光唇鱼群体遗传学特征
Ne、He、Ho和PIC等参数是衡量群体遗传变异程度、遗传信息大小,指示遗传多态性的重要指标,各数值越高,则群体遗传多样性越高,对环境的适应力越强,在生长、繁殖性能上也更具培育优势[25-27]。群体遗传分析结果显示,本研究在MC4R基因检测出的15个SNP位点中,除G669C外,其余14个SNP位点的Ne、PIC和Ho均处于较高水平,属中度多态性,群体中等位基因分布均匀。
Fis是以观测杂合频率与期望杂合频率的差异性反映群体间的近交程度,也被称为HWE平衡偏离系数。Fis值越趋近于0,群体越趋于HWE平衡,当Fis的值小于0时,Ho>He,群体内杂合子较多;反之,则群体纯合子更多[28]。本研究对15个SNP位点进行Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验,结果显示除位点G669C外,其余14个位点P值均小于0.01,Fis值接近于−1,处于Hardy-Weinberg极不平衡状态,种群中杂合子过剩。杂合子过剩是养殖群体较为常见的现象,人工选择压力、非随机交配、亲本数量限制、种群大小和结构变化等因素是造成养殖群体杂合子过剩而偏离Hardy-Weinberg平衡的主要原因[29],如团头鲂(Megalobrama amblycephala)等养殖群体也存在杂合子过剩现象[30-32]。此外,本研究杂合子过剩也可能与样本量相对较少,且样本体长、体质量等表型存在较大差异有关。本研究中软鳍新光唇鱼群体杂合子过剩,表明其正经历人工选育过程,与实际养殖、选育情况相符,一定程度上证明了本研究筛选生长相关SNP位点的可靠性与真实性较高。
3.2 SNP位点筛选及与生长性状的关联性
本研究对MC4R基因扩增后产物采取直接测序法进行SNP位点的筛选,MC4R基因筛选出15个SNP位点。MC4R基因一级结构预测分析发现,15个SNP位点中,仅G227A位点出现错义突变,所在序列由GTC变为ATC,导致氨基酸种类由缬氨酸(V)变为异亮氨酸(I),其余位点同属同义突变,虽然同义突变不能通过氨基酸突变直接改变蛋白质的结构和功能,但仍可以改变mRNA二级结构、翻译效率而影响生物体表型[33-34],此结论也在后续软鳍新光唇鱼生长表型的关联性分析中得到印证。
MC4R基因的15个SNP位点与软鳍新光唇鱼主要生长性状关联分析结果显示13个SNP位点与个体体长、体质量具有不同程度的相关性。其中,G227A、A322G、C364T、G403A、T451C、G457A 、G472A、T484C、G520A、T583C、G736A、C775G等12个SNP位点与体长、体质量显著相关,且均以纯合子为优势基因型,分别为AA、GG、TT、AA、CC、AA、AA、CC、AA、CC、AA、GG型;位点C664T检测到CC、CT两种基因型,虽以杂合子CT型为优势基因型,但仅与体质量显著相关。MC4R基因的多态性与性状关联研究在畜牧中开展较早且更广泛,虽然在尼罗罗非鱼 (Oreochromis niloticus)[35]、红鳍东方鲀(Takifugu rubripes)[36]、光倒刺鲃(Spinibarbus hollandi)[37]中筛选出多个SNP位点,但较少与鱼类的生长性状显著相关,研究更多集中在基因克隆、组织表达[38-41]。不同群体以杂合子或以纯合子为优势基因型,在许多研究中也有报道,如黄李勇等[42]在对巴什拜羊(Ovis aries)MC4R基因与生长性状关联分析中检测出GC和GG两种基因型,并以GC型为群体的优势基因型;周艳等[43]在5个地方鸡种MC4R基因的研究中检测出g.54 C>G、g.315 G>T两处SNP位点,且两位点在各群体中均主要以纯合子为优势基因型。因此,本研究结果支持MC4R基因存在丰富的SNP位点,且对软鳍新光唇鱼的生长性状具有显著影响,可以将其作为鱼类分子育种研究的候选基因进一步挖掘。
4. 结论
本研究通过直接测序法在软鳍新光唇鱼MC4R基因2个拷贝中检测出15个SNP位点,遗传多样性分析表明该养殖群体具有较高的遗传丰富度,能够作为良种选育的候备种群,同时利用关联性分析筛选出13个SNP位点与生长性状显著相关,为今后软鳍新光唇鱼生长相关机制和分子标记的进一步解析,以及生长性状的改良提供了科学依据。
-
表 1 软鳍新光唇鱼PCR引物信息
Table 1 Primers used in the amplification of N. benasi
目标基因
Gene of interest引物
Primers序列(5’-3’ )
Sequence (5’-3’)退火温度/℃
Annealing temperature产物长度/bp
Product lengthMC4R M1 F:AAACCACTGACTACGGATAT
R:CGTCAAACAGAAACAAGC55 1 027 M2 F:AAACCACTGACTACGGATAT
R:TTGCTTAGTGTTGTCTTGC55 1 050 表 2 MC4R基因两个拷贝SNP位点的氨基酸突变
Table 2 Amino acid mutations at various SNP loci in two copies of the MC4R gene
位点
Loci突变序列
Mutant sequences突变氨基酸类型
Types of mutant amino acid突变区
RegionG669C CGG→CGC R-R 精氨酸 exon G227A GTC→ATC V-I 缬氨酸−异亮氨酸 exon A322G ACA→ACG T-T 苏氨酸 exon C364T CGC→CGT R-R 精氨酸 exon G403A TCG→TCA S-S 丝氨酸 exon T451C ATT→ATC I-I 异亮氨酸 exon G457A GTG→GTA V-V 缬氨酸 exon G472A ACG→ACA T-T 苏氨酸 exon T484C GCT→GCC A-A 丙氨酸 exon G520A GCG→GCA A-A 丙氨酸 exon T583C TAT→TAC Y-Y 酪氨酸 exon C664T CAC→CAT H-H 组氨酸 exon G736A GCG→GCA A-A 丙氨酸 exon C742T AAC→AAT N-N 天冬酰胺 exon C775G CTC→CTG L-L 亮氨酸 exon 表 3 MC4R基因两个拷贝各SNP位点群体遗传信息
Table 3 Population genetic information of each SNP locus of two copies of MC4R gene
位点
Loci样本数
Number基因型(频率)
Genotypes (frequency)等位基因(频率)
Aelles (frequency)HWE Ne Ho He Fis PIC G669C 74 GG(0.635)
GC(0.351)
CC(0.014)C(0.189)
G(0.811)X2=1.443
(P=0.230)1.443 0.351 0.309 −0.145 0.260 G227A 65 AA(0.064)
GG(0.095)
GA(0.841)G(0.516)
A(0.484)X2=28.813
(P=0.000)1.998 0.841 0.504 −0.684 0.375 A322G 65 AA(0.077)
GG(0.062)
GA(0.861)G(0.492)
A(0.507)X2=33.300
(P=0.000)2.000 0.862 0.504 −0.724 0.375 C364T 53 CC(0.113)
TT(0.076)
CT(0.811)C(0.519)
T(0.481)X2=20.077
(P=0.000)1.997 0.811 0.504 −0.625 0.375 G403A 66 GG(0.106)
AA(0.061)
GA(0.833)C(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=28.970
(P=0.000)1.996 0.833 0.503 −0.670 0.375 T451C 65 CC(0.062)
TT(0.077)
CT(0.861)C(0.476)
A(0.524)X2=33.300
(P=0.000)2.000 0.862 0.504 −0.724 0.375 G457A 66 GG(0.076)
GA(0.864)
AA(0.060)G(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=34.220
(P=0.000)2.000 0.864 0.504 −0.728 0.375 G472A 62 GG(0.081)
GA(0.855)
AA(0.064)G(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=30.555
(P=0.000)2.000 0.855 0.504 −0.841 0.373 T484C 64 CC(0.062)
TT(0.078)
CT(0.860)C(0.492)
T(0.508)X2=32.383
(P=0.000)2.000 0.859 0.504 −0.719 0.375 G520A 63 GG(0.063)
AA(0.080)
GA(0.857)G(0.508)
A(0.492)X2=31.468
(P=0.000)2.000 0.857 0.504 −0.715 0.375 T583C 59 CC(0.068)
TT(0.085)
CT(0.847)C(0.492)
T(0.508)X2=27.837
(P=0.000)1.999 0.848 0.504 −0.695 0.375 C664T 62 CC(0.097)
CT(0.903)C(0.548)
T(0.452)X2=41.238
(P=0.000)1.981 0.903 0.499 −0.824 0.373 G736A 66 GG(0.076)
AA(0.061)
GA(0.863)G(0.492)
A(0.508)X2=34.220
(P=0.000)2.000 0.864 0.504 −0.728 0.375 C742T 66 CC(0.076)
CT(0.924)C(0.540)
T(0.460)X2=47.867
(P=0.000)1.989 0.924 0.501 −0.826 0.374 C775G 66 CC(0.076)
GG(0.061)
GC(0.863)C(0.508)
G(0.492)X2=34.220
(P=0.000)2.000 0.864 0.504 −0.728 0.375 注:HWE为哈代温伯格平衡;He为期望杂合度;Ho为观测杂合度;Ne为有效等位基因数;PIC为多态信息含量;Fis为固定指数。 Notes: HWE indicates Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium; He indicates expected heterozygosity; Ho indicates observed heterozygosity; Ne indicates eff-ective number of alleles; PIC indicates polymorphism information content; Fis indicates fixation index. 表 4 MC4R基因两个拷贝SNP位点各基因型与生长性状关联性分析
Table 4 Association analysis between different genotypes of loci of two copies of SNP MC4R gene and growth traits
位点
Loci基因型(样本量)
Genotype(n)体质量/g
Body mass体长/mm
Body length全长/mm
Total lengthG669C GC(26)
GG(47)
CC(1)8.55±9.55a
14.25±10.97a
27.84±0.00a68.78±22.35a
82.89±26.30a
106.90±0.00a85.66±26.87a
101.69±30.29a
132.73±0.00aG227A GG(6)
AA(4)
GA(53)3.59±0.46b
26.13±2.13a
13.77±10.93b58.73±2.02b
109.92±5.41a
81.06±25.56b74.12±2.89b
134.23±5.46a
100.71±30.81bA322G AA(5)
GG(4)
GA(56)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
13.67±10.96b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
80.81±25.52b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
100.44±30.72aC364T CC(6)
CT(43)
TT(4)3.58±0.46b
14.82±10.96b
26.13±2.13a59.00±1.90b
83.70±25.32b
109.92±5.41a74.42±2.82b
103.80±30.42b
134.23±5.46aG403A GG(7)
GA(55)
AA(4)3.66±0.45b
13.85±10.98b
26.13±2.13a59.29±1.81b
81.19±25.60b
109.92±5.41a74.60±2.64b
100.88±30.82b
134.23±5.46aT451C TT(5)
CT(56)
CC(4)3.57±0.51b
13.31±10.94b
26.13±2.13a59.02±2.12b
79.98±25.44b
109.92±5.41a74.38±3.15a
99.43±30.63a
134.23±5.46aG457A GG(5)
GA(57)
AA(4)3.57±0.51b
13.50±10.94b
26.13±2.13a59.02±2.12b
80.44±25.45b
109.92±5.41a74.38±3.15a
99.98±30.64a
134.23±5.46aG472A GG(5)
GA(53)
AA(4)3.57±0.51b
13.73±10.88b
26.13±2.13a59.02±2.12b
80.89±25.49b
109.92±5.41a74.38±3.15b
100.49±30.67b
134.23±5.46aT484C CC(4)
TT(5)
CT(55)26.13±2.13a
3.57±0.51b
12.86±10.59b109.92±5.41a
59.02±2.12b
79.19±25.01b134.23±5.46a
74.38±3.15b
98.44±30.07bG520A GG(5)
AA(4)
GA(54)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
12.86±10.81b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
79.06±25.40b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
98.27±30.54aT583C CC(4)
TT(5)
CT(50)26.13±2.13a
3.57±0.51b
12.70±10.83b109.92±5.41a
59.02±2.12b
78.51±25.34b134.23±5.46a
74.38±3.15b
97.60±30.47bC664T CC(6)
CT(56)3.41±0.60b
14.64±11.14a58.21±2.75a
83.01±25.96a73.50±3.55a
102.90±31.09aG736A GG(5)
AA(4)
GA(57)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
13.50±10.94b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
80.44±25.45b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
99.98±30.64aC742T CC(5)
CT(61)3.57±0.51a
14.33±11.04a59.02±2.12a
82.37±25.69a74.38±3.15a
102.22±30.83aC775G CC(5)
GG(4)
GC(57)3.57±0.51b
26.13±2.13a
13.50±10.94b59.02±2.12b
109.92±5.41a
80.44±25.45b74.38±3.15a
134.23±5.46a
99.98±30.64a注:同一位点同一指标不同上标小写字母表示组内差异显著(P<0.05),相同上标字母表示组内差异不显著(P>0.05)。 Note: Different superscript lowercase letters in the same column of locus indicate significant difference within the group (P<0.05), and the same superscript lowercase letters indicate no significant differences within the group (P>0.05). -
[1] 褚新洛,陈银瑞. 云南鱼类志(上册)[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1989:175 − 176. Chu X L, Chen Y R. Fishes of Yunnan Province (I) [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 175 − 176.
[2] 杨剑,潘晓赋,陈小勇,等. 李仙江鱼类资源的现状与保护对策[J]. 水生态学杂志,2010,3(2):54 − 60. Yang J, Pan X F, Chen X Y, et al. Status and conservation strategy of fish resources in Lixianjiang River[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2010, 3(2): 54 − 60.
[3] 杨永宏,杨君兴,潘晓赋,等. 云南李仙江流域水电开发中的鱼类资源保护[J]. 动物学研究,2011,32(2):188 − 195. Yang Y H, Yang J X, Pan X F, et al. Fishery resource protection by artificial propagation in hydroelectric development: Lixianjiang River drainage in Yunnan as an example[J]. Zoological Research, 2011, 32(2): 188 − 195.
[4] 王晓爱,杨君兴,陈小勇,等. 软鳍新光唇鱼精子的超低温冷冻保存[J]. 动物学研究,2012,33(3):283 − 289. Wang X A, Yang J X, Chen X Y, et al. Cryopreservation of sperm from Neolissochilus benasi[J]. Zoological Research, 2012, 33(3): 283 − 289.
[5] 潘晓赋,刘倩,王晓爱,等. 软鳍新光唇鱼(Neolissochilus benasi)的人工繁殖与胚胎发育[J]. 动物学研究,2013,34(6):617 − 625. Pan X F, Liu Q, Wang X A, et al. Artificial propagation and embryonic development of Neolissochilus benasi[J]. Zoological Research, 2013, 34(6): 617 − 625.
[6] 潘亚丹,鲁翠云,孙志鹏,等. 梭鲈快速生长品系F3基因型与生长性状关联分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报,2024,33(5):1053 − 1063. Pan Y D, Lu C Y, Sun Z P, et al. Correlation analysis between genotypes and growth traits of fast growing strain F3 of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca)[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2024, 33(5): 1053 − 1063.
[7] Yue G H. Recent advances of genome mapping and marker-assisted selection in aquaculture[J]. Fish and Fisheries, 2014, 15(3): 376 − 396. DOI: 10.1111/faf.12020
[8] 殷艳慧,蒋万胜,潘晓赋,等. 水产养殖鱼类生长性状研究进展[J]. 中国水产科学,2020,27(4):463 − 484. Yin Y H, Jiang W S, Pan X F, et al. Recent progress in growth trait of aquaculture fish[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2020, 27(4): 463 − 484.
[9] Yeo G S, Farooqi I S, Challis B G, et al. The role of melanocortin signalling in the control of body weight: evidence from human and murine genetic models[J]. QJM-an International Journal of Medicine, 2000, 93(1): 7 − 14. DOI: 10.1093/qjmed/93.1.7
[10] Sinha P S, Schiöth H B, Tatro J B. Roles of the melanocortin-4 receptor in antipyretic and hyperthermic actions of centrally administered alpha-MSH[J]. Brain Research, 2004, 1001(1−2): 150 − 158. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2003.12.007
[11] Haskell-Luevano C, Monck E K. Agouti-related protein functions as an inverse agonist at a constitutively active brain melanocortin-4 receptor[J]. Regulatory Peptides, 2001, 99(1): 1 − 7. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-0115(01)00234-8
[12] Gantz I, Miwa H, Konda Y, et al. Molecular cloning, expression, and gene localization of a fourth melanocortin receptor[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1993, 268(20): 15174 − 15179. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)82452-8
[13] Mountjoy K G, Mortrud M T, Low M J, et al. Localization of the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4-R) in neuroendocrine and autonomic control circuits in the brain[J]. Molecular Endocrinology, 1994, 8(10): 1298 − 1308.
[14] Sheridan M A, Hagemeister A L. Somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in fish growth[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2010, 167(3): 360 − 365. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.09.002
[15] 李星润,兰国湘,王孝义,等. 猪MC4R基因Asp298Asn位点多态性及其与生长性状的关联[J]. 畜牧与兽医,2016,48(2):23 − 27. Li X R, Lan G X, Wang X Y, et al. Polymorphism of Asp298Asn site in the porcine MC4R gene and its association with growth traits[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 48(2): 23 − 27.
[16] Choi J S, Jin S K, Jeong Y H, et al. Relationships between single nucleotide polymorphism markers and meat quality traits of duroc breeding stocks in Korea[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2016, 29(9): 1229 − 1238. DOI: 10.5713/ajas.16.0158
[17] 奥斯伯 F M,布伦特 R,金斯顿 R E,等. 精编分子生物学实验指南[M]. 颜子颖,王海林,译. 北京:科学出版社,1998:30−31. Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, et al. Short protocols in molecular biology[M]. Yan Z Y, Wang H L, trans. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 30−31.
[18] Wagner A, Silva-santos A R, Rosa S S, et al. Primary purification of plasmid DNA using differential isopropanol precipitation[M]//Sousa Â. DNA vaccines: methods and protocols. New York: Humana, 2021: 151−165.
[19] Burland T G. DNASTAR's Lasergene sequence analysis software[M]//Misener S, Krawetz S A. Bioinformatics methods and protocols. Totowa: Humana Press, 2000: 71 − 91.
[20] Yeh F C, Boyle T J B. Population genetic analysis of codominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits[J]. Belgian Journal of Botany, 1997, 129: 157 − 163.
[21] Liu K J, Muse S V. PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis[J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(9): 2128 − 2129. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
[22] SPSSAU. The SPSSAU project (2020) (version 20.0)[online application software][EB/OL]. [2024-12-10]. https://www.spssau.com.
[23] Hearne C M, Ghosh S, Todd J A. Microsatellites for linkage analysis of genetic traits[J]. Trends in Genetics, 1992, 8(8): 288 − 294. DOI: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90256-4
[24] Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, et al. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms[J]. American Journal of Human Genetics, 1980, 32(3): 314 − 331.
[25] Nei M, Maruyama T, Chakraborty R. The bottleneck effect and genetic variability in populations[J]. Evolution, 1975, 29(1): 1 − 10. DOI: 10.2307/2407137
[26] Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals[J]. Genetics, 1978, 89(3): 583 − 590. DOI: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583
[27] Beardmore J A, Mair G C, Lewis R I. Biodiversity in aquatic systems in relation to aquaculture[J]. Aquaculture Research, 1997, 28(10): 829 − 839. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.1997.tb01007.x
[28] Wright S. Evolution and the genetics of populations, volume 4: variability within and among natural populations[M]. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1984.
[29] Waples R S. Testing for Hardy–Weinberg proportions: have we lost the plot?[J]. Journal of Heredity, 2015, 106(1): 1 − 19. DOI: 10.1093/jhered/esu062
[30] 袁吉贵,刘丽,陈增祥,等. 吉富罗非鱼第二十一代选育群体微卫星标记研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2017,36(4):1498 − 1504. Yuan J G, Liu L, Chen Z X, et al. Microsatellite marker research of the twenty-one generation breeding population of GIFT strains of Oreochromis niloticus[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2017, 36(4): 1498 − 1504.
[31] Wigginton J E, Cutler D J, Abecasis G R. A note on exact tests of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium[J]. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 2005, 76(5): 887 − 893. DOI: 10.1086/429864
[32] 徐湛宁,李福贵,郑国栋,等. 团头鲂耐低氧新品系雌核发育群体遗传结构的微卫星分析[J]. 水产学报,2017,41(3):330 − 338. Xu Z N, Li F G, Zheng G D, et al. Analysis of genetic structure of gynogenetic population in new strain of hypoxia-tolerant Megalobrama amblycephala using microsatellite markers[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2017, 41(3): 330 − 338.
[33] Bali V, Bebok Z. Decoding mechanisms by which silent codon changes influence protein biogenesis and function[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2015, 64: 58 − 74.
[34] Sharma Y, Miladi M, Dukare S, et al. A pan-cancer analysis of synonymous mutations[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2569. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10489-2
[35] 刘福平,白俊杰,叶星,等. 罗非鱼MC4R基因克隆及与其生长相关的SNPs位点[J]. 中国水产科学,2009,16(6):816 − 823. Liu F P, Bai J J, Ye X, et al. Cloning of MC4R gene and study on the association between SNPs of MC4R and growth trait in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2009, 16(6): 816 − 823.
[36] 张丽,仇雪梅,王娟,等. 红鳍东方鲀(Takifugu rubripes)MC4R基因的多态性分析[J]. 生物技术通报,2012(7):97 − 102. Zhang L, Qiu X M, Wang J, et al. Polymorphism analysis on melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) gene in Takifugu rubripes[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2012(7): 97 − 102.
[37] Yang Y, Li Q, Shu H, et al. Characterization of the melanocortin-4 receptor gene from Spinibarbus hollandi and the association between its polymorphisms and S. hollandi growth traits[J]. Fisheries Science, 2017, 83(6): 967 − 976. DOI: 10.1007/s12562-017-1125-x
[38] Wan Y M, Zhang Y, Ji P F, et al. Molecular characterization of CART, AgRP, and MC4R genes and their expression with fasting and re-feeding in common carp (Cyprinus carpio)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012, 39(3): 2215 − 2223. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-011-0970-4
[39] 费飞,孙少阳,姚玉霄,等. lepr和mc4r基因突变斑马鱼的制备及表型分析[J]. 生理学报,2017,69(1):61 − 69. Fei F, Sun S Y, Yao Y X, et al. Generation and phenotype analysis of zebrafish mutations of obesity-related genes lepr and mc4r[J]. Acta Physiologica Sinica, 2017, 69(1): 61 − 69.
[40] Li L, Yang Z, Zhang Y P, et al. Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and pharmacological characterization of melanocortin-4 receptor in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Domestic Animal Endocrinology, 2017, 59: 140 − 151. DOI: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2016.11.004
[41] 黄露. 翘嘴红鲌mc3r、mc4r和mrap2的基因克隆、表达分析及功能初步研究[D]. 长沙:湖南师范大学,2021. Huang L. Gene cloning, expression analysis and preliminary functional studies of mc3r, mc4r and mrap2 in topmouth culter[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2021.
[42] 黄李勇,赵雄,曼则热·朱尔丁,等. 巴什拜羊MC4R基因多态性及其与生长性状的关联分析[J]. 草食家畜,2018(3):17 − 23. Huang L Y, Zhao X, Manzere Z, et al. Association analysis of single nucleotide polymormhism of MC4R gene with growth traits in Bashibai sheep[J]. Grass-feeding Livestock, 2018(3): 17 − 23.
[43] 周艳,雷秋霞,韩海霞,等. 黑素皮质素受体4(MC4R) 基因在5个地方鸡种中的遗传多态性分析[J]. 山东农业科学,2017,49(8):127 − 130. Zhou Y, Lei Q X, Han H X, et al. Genetic polymorphism analysis on MC4R gene in five Chinese indigenous chicken breeds[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 49(8): 127 − 130.



 下载:
下载: